In the previous article, we introduced that digital signals can only represent infinite analog signals with a limited combination of 0/1, so quantization must be accomplished through the Sample Rate and Bit Depth. So, what are the sampling rate and bit depth?
In layman's terms, the sampling rate refers to the number of times an analog sound waveform is "sampled" per second, with the unit being Hertz (Hz).
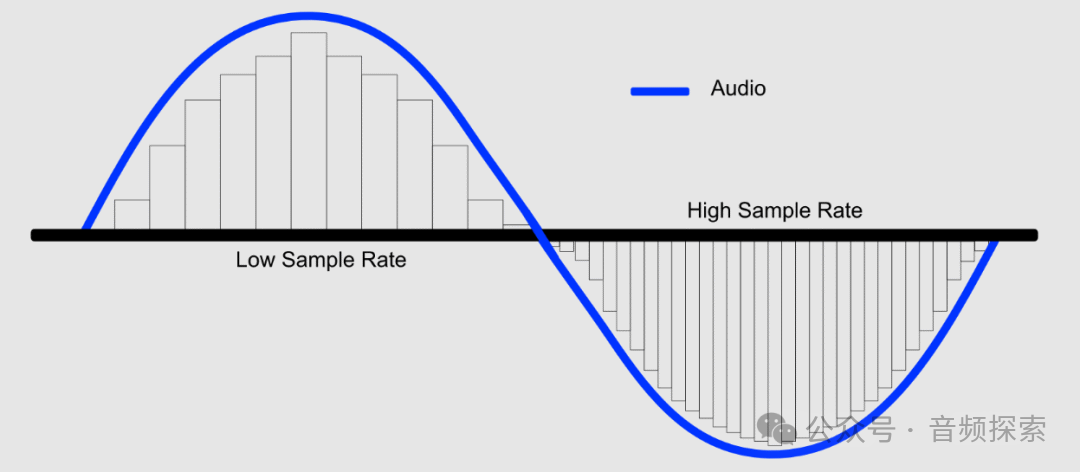
The sampling rate determines the highest frequency that can be recorded. One of the core theories in the field of digital audio, the Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem, tells us that to fully reproduce an analog signal, the sampling rate must be greater than twice the highest frequency in the signal.
We know that the auditory range of the human ear is approximately 20Hz to 20kHz. Theoretically, when the sampling rate is set to 40kHz, it can reproduce the frequency that the human ear can hear without distortion. Then what problems will arise if the sampling rate is not high enough? The answer is that the "Aliasing" phenomenon will occur, that is, high-frequency components will be misjudged as low-frequency signals, resulting in sound distortion. For instance, if we record a 20kHz sound with a sampling rate of 30kHz, since the sampling rate is insufficient to capture its complete variation, this high frequency will be wrongly "mapped" to a lower frequency band, making it sound as if there are some inexplicable low or mid-frequency sounds added. In practical applications, to leave a buffer zone for anti-aliasing filters, the commonly set sampling rate is 44.1kHz or 48kHz, rather than exactly 40kHz.
In music production, the sampling rates we commonly use include 44.1kHz, 48kHz, 96kHz, etc.
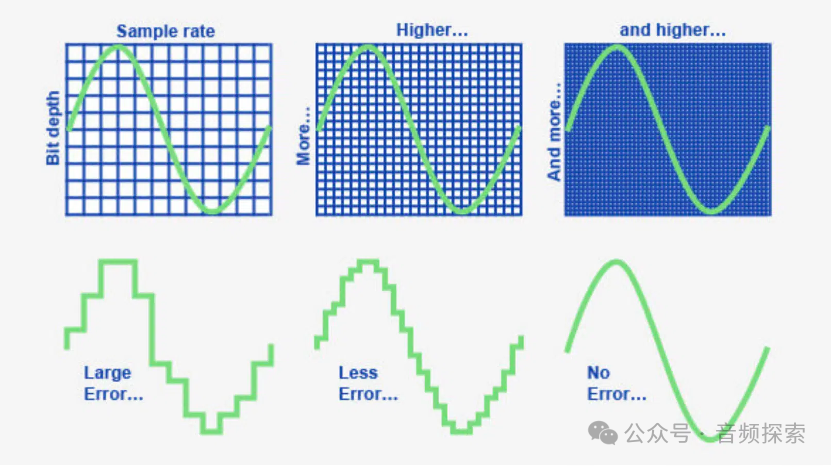
T he commonly used 16-bit corresponds to a dynamic range of approximately 96dB and is the standard for CD audio. 24-bit corresponds to a dynamic range of approximately 144dB and is a commonly used specification in professional recording and mixing. It should be said that 16-bit is already sufficient for music playback. However, in the recording and production stages, 24-bit offers greater operational space and higher fidelity, and thus has become the mainstream in the industry.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


