In circuit design, there are all kinds of power symbols, which often confuse people. Today, I have sorted out 27 of them and would like to share them with everyone.
The following "V" stands for "Volatge".
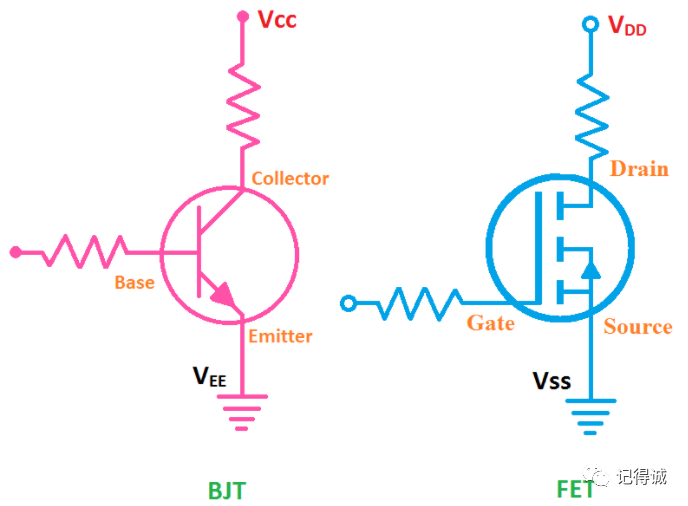
1. VCC: C can be understood as the Collector of a transistor or a Circuit, referring to the positive terminal of the power supply.
2. VDD: D can be understood as the Drain or Device of a MOSFET, referring to the positive terminal of the power supply.
3. VEE: E can be understood as the Emitter of a transistor, referring to the negative terminal of the power supply.
4. VSS: S can be understood as the Source of the MOSFET, referring to the negative terminal of the power supply.
5. VBB: B can be understood as the base B of a transistor, generally referring to the positive terminal of a power supply.
Just take a look at the picture below and you'll understand the above five.
6. AVCC, where A stands for Analog, is used to simulate VCC. Generally, analog devices have it.
7. AVDD, where A stands for Analog, is used to simulate VDD. Generally, analog devices do this
8. DVCC, where the "D" stands for Digital, or Digital VCC, is typically found in digital circuits.
9. DVDD, where D stands for Digital, or Digital VDD, is typically used in digital circuits.
For the above four, if the circuit or device has no distinction between analog and digital, then VCC and VDD are used.
10. Youdaoplaceholder0, simulate GND, corresponding to the negative terminal of AVCC or AVDD.
11. DGND, the digit GND, corresponds to the negative terminal of DVCC or DVDD.
12. PGND, where P stands for Power, is a power GND. For instance, in DC-DC, there will be a distinction between the power ground and the signal.
The above three are essentially GND. The distinction is more for the requirements of PCB routing. There are some single-point grounding or multi-point grounding treatments to avoid interference.
13. Vpp, sometimes it seems to be called Vpk, is the peak-to-peak voltage. For sinusoidal signals, it is the peak voltage minus the trough voltage, and the maximum value minus the minimum value.
14. Vrms, rms is the abbreviation of root mean squre, meaning root mean square. Generally, Vrms refers to the effective value of an alternating current signal.
15. VBAT, where BAT is the abbreviation of BATTERY, generally refers to battery voltage.
16. VSYS, where SYS is the abbreviation of SYSTEM, generally refers to the system power supply of a platform solution (such as MTK).
17. VCORE, where CORE means core, generally refers to the nuclear voltage of chips such as CPU and GPU.
18. VREF, where REF stands for reference, refers to the reference voltage, such as the reference voltage inside an ADC, etc.
19. PVDD, where P stands for Power, power VDD.
20. CVDD, where the "C" stands for "CORE", which means nuclear power supply (VDD).
21. IOVDD, where IO stands for GPIO, refers to the VDD that supplies power to GPIO. It is used in cameras and serves as the pull-up power supply for I2C communication.
22. DOVDD, used in the CAMERA, is supplied to the CAMERA from the outside and is usually also an analog power supply.
23. AFVDD, Auto Focus VDD, meaning automatic focus VDD power supply, is used in cameras and is used to power the motor.
24. VDDQ is used in DDR. There is a DQ signal in DDR, which can be understood as powering these data signals.
25. VPP, this VPP is all in capital letters. It is used in DDR4 but not in DD3. It is called activation voltage, the turn-on voltage of the bit line.
26. VTT, generally VTT=1/2VDDQ, is also used in DDR to provide power for some control signals.
27. VCCQ is used in nand flash, such as the commonly used eMMC and UFS memory in mobile phones, and is generally used to power IO.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


