
Current control mode and waveform:
Square wave drive: In each commutation cycle, the current in the stator winding is switched to the high or low two states, forming a rectangular wave. Usually a six-step commutation method is used, that is, every 60 degrees of electrical Angle to change the phase once, resulting in torque.

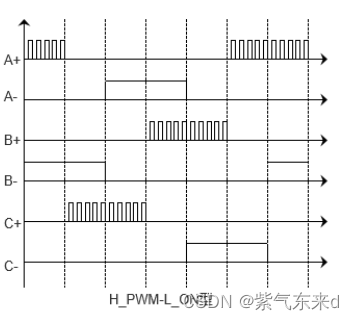
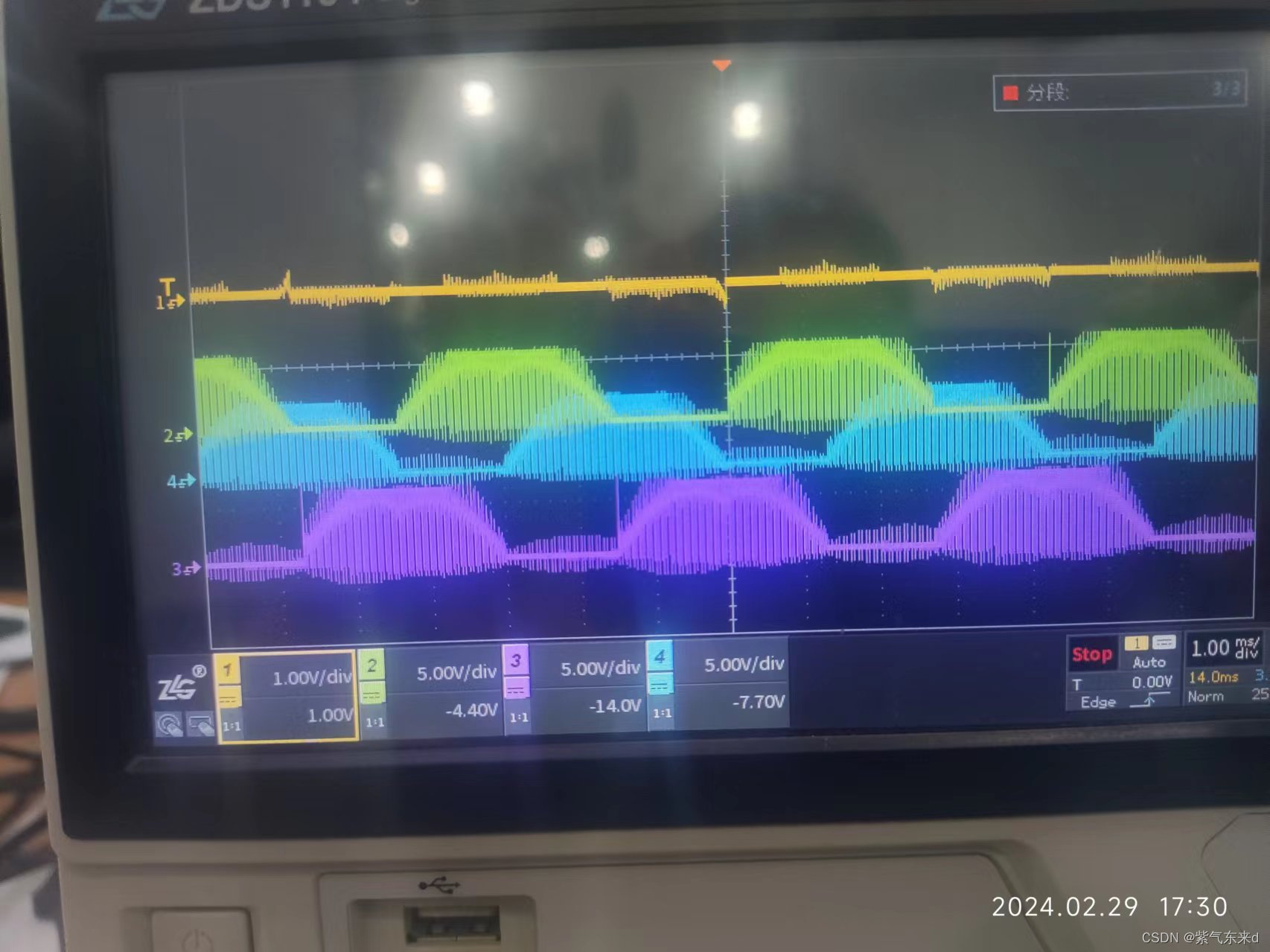
Sine wave drive: The current flowing through the stator winding is in the form of an analog sine wave, and its amplitude, frequency and phase are closely related to the rotor position.

Magnetic field oriented control (FOC) technology is used to control the current accurately.
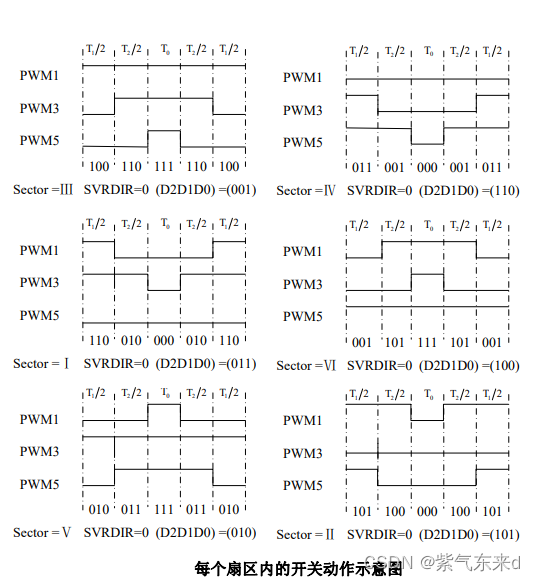
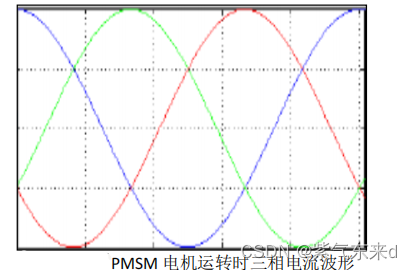
Mechanical characteristic
Square wave drive:
Torque output: Due to the discontinuity of current switching, the torque change is step like, and the torque ripple is large, especially at low speeds, which may lead to high vibration and noise. Efficiency and loss: High speed operation may reduce efficiency due to electromagnetic interference caused by current chopping and increased core loss. Sine wave drive:
Torque output: The current waveform is synchronized with the flux trajectory, and the torque produced is closer to the ideal continuous and uniform, so the torque ripple is small, the smoothness and accuracy are higher, and the vibration and noise are lower. Efficiency and loss: Through optimized current control, the overall efficiency is higher, especially in the wide speed range can maintain high efficiency, and reduce unnecessary iron and copper losses. Control system complexity:
Square wave drive: The control strategy is relatively simple, generally using Hall sensors to detect the rotor position, and the controller design cost is low. Sine wave drive: Complex FOC algorithms are required to calculate stator current instructions in real time to track the desired flux and torque, while advanced position sensors (such as encoders or rotary transformers) are required to provide accurate position information, resulting in increased complexity and cost of control system hardware and software. Application:
Square wave drive: suitable for low-cost, low torque ripple and noise requirements of industrial equipment, such as household appliances, small power tools, etc. Sine wave drive: widely used in high-end precision fields, including servo systems, robot joints, electric vehicle drive motors, aerospace and various occasions with high dynamic performance requirements, especially suitable for applications with strict requirements for speed control accuracy, torque response speed and efficiency. Performance comparison:
Starting performance: Both provide good starting torque, but the sine wave drive provides finer control of the torque curve during the starting phase, helping to reduce impact loads. Dynamic response: Because of its smooth current control, the sine wave drive performs better in the process of rapid acceleration and deceleration, which can effectively improve the dynamic performance and stability of the system.
In summary, the main difference between square wave driven brushless motors and sine wave driven brushless motors is the difference in drive control technology and the resulting motor performance. Users should choose the most suitable drive scheme according to the needs of the actual application, weighing factors such as cost, performance, efficiency and reliability.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


