Source: ON Mei Author: Jinchang Zhou, Product Line Manager
Electrification is popular as manufacturers and consumers alike try to wean themselves off fossil fuel energy. This has important implications for protecting the environment, limiting pollution and slowing the destructive global warming trend. Electric vehicles (EVs) are growing in popularity around the world, and numerous companies have entered the field trying to convert commercial and agricultural vehicles (CAVs) to be powered by electricity.
However, this shift has led to a rapid increase in demand for electricity, putting extreme pressure on the grid. Despite their high energy efficiency, applications such as electric vehicles, data centers, and heat pumps still require significant amounts of energy to operate.
New renewable energy sources such as solar, wind and wave energy have been widely welcomed and are gradually becoming mainstream. Only applications that use entirely renewable energy can be considered truly "clean."
The solar market has been developing for many years and is relatively mature. According to a report by Fortune Business Insights, the solar market is estimated at $273 billion today and is expected to grow to $436 billion by 2032. In 2023, North America will account for more than 40% of the solar market.
Power conversion challenges in renewable energy applications
Solar power generation is growing rapidly. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), in 2022, the amount of electricity generated by solar energy increased by 26% over the previous year, reaching 1,300 TWh. This marks the moment when solar power has surpassed wind power as the largest source of renewable electricity.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels generate direct current (DC), while the grid requires alternating current (AC), so central PV inverters are an integral part of large grid-connected installations. All the energy generated by photovoltaic panels passes through the inverter, so the efficiency of the inverter has an important impact. Although solar energy is inexhaustible, inefficient conversion results in very limited energy being delivered to the grid. The energy wasted in the process is converted into heat, which in turn poses a serious challenge because many solar installations are typically located in sunny, warmer environments, such as deserts.
Cost is also a very important consideration, which can directly affect consumers' electricity bills and the profitability of power companies. To achieve higher power, many central inverters use multiple conversion modules in parallel, the number of which is determined by the power rating of each module. The higher the power capacity of each module, the fewer modules are required, thus reducing costs.
While electric vehicles have come a long way, CAVs have been slow to make the transition to electric drive. Cavs are larger, consume more fuel and produce more emissions per trip, accounting for 28% of all greenhouse gas emissions from transportation, although they make up only 2% of the total number of vehicles. While the electrification of commercial passenger vehicles (such as buses) is beginning to pay off, most large trucks, construction machinery and agricultural vehicles (such as tractors) still rely on diesel. Now, things are starting to change. In order to meet stringent zero-emission regulations in global markets such as the European Union, China and California, the share of electric trucks (pure electric and hybrid) sales is expected to increase from 5% today to 40-50% by 2030.
Compared to fossil fuel commercial vehicles, electric commercial vehicles have simpler construction and fewer moving parts. In the case of the same load capacity, electric vehicles are smaller, more reliable and less maintenance-related costs. Battery costs are now significantly reduced, and the total cost of ownership for an electric CAV is now lower than for an internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle.
Similar to solar applications, efficiency is also a key requirement for electric CAVs. Each car has limited battery power, and the more efficient the conversion process in the inverter, the longer the vehicle will travel. Or travel the same distance requires less power.
Given our reliance on solar and electric CAVs in the future, reliability naturally becomes very important.
Advanced power technology for inverter applications
In high-power applications such as three-phase solar photovoltaic inverters, three-level active neutral clamp (ANPC) converters are a more common topology. This multilevel topology is specifically designed to improve system performance and efficiency.
Common neutral clamp (NPC) converters use diodes to connect the neutral point of a DC link capacitor to the output. In an ANPC configuration (Figure 1), clamping is performed by a switch, thereby improving control, reducing switching losses and increasing efficiency, and correspondingly reducing the need for heat dissipation measures, contributing to a smaller, less costly solution.
The topology arrangement reduces the voltage stress on the individual switches, thus improving reliability. In addition, ANPC enables grid friendly waveforms.
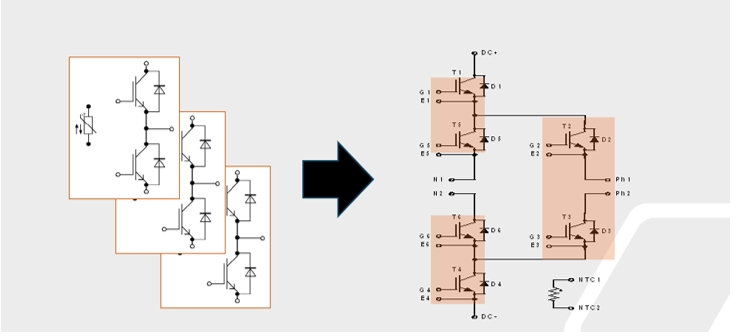
Design engineers can create high-performance three-level active neutral clamp modules by paralleling multiple power modules, such as onsemi's QDual 3 IGBT module, with system outputs ranging from 1.6 MW to 1.8 MW.

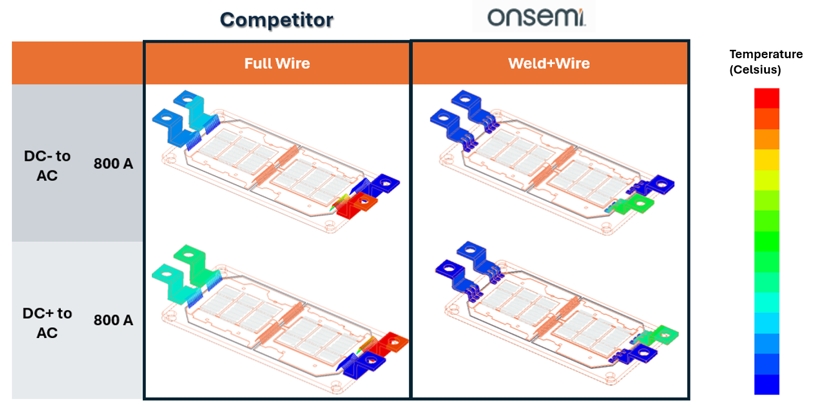
Reliability is key for solar and CAV applications, so how modules are constructed and tested is critical. For example, while there are many similar solutions that use lead bonding to secure terminals, On chose to use ultrasound to weld the modules. The latter helps increase current carrying capacity, provides a better heat dissipation path, and is more robust than the former (Figure 4).
On's new high power QDual3 technology
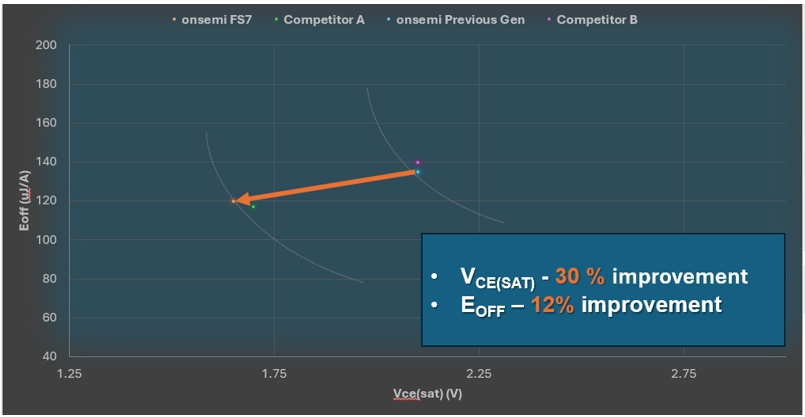
Dedicated QDual 3-half-bridge IGBT module NXH800H120L7QDSG is suitable for central solar inverter, energy storage system (ESS), uninterruptible power supply (UPS). SNXH800H120L7QDSG is suitable for CAV. Both devices are based on FS7 technology with improved VCE(SAT) and EOFF, resulting in reduced losses and improved energy efficiency.
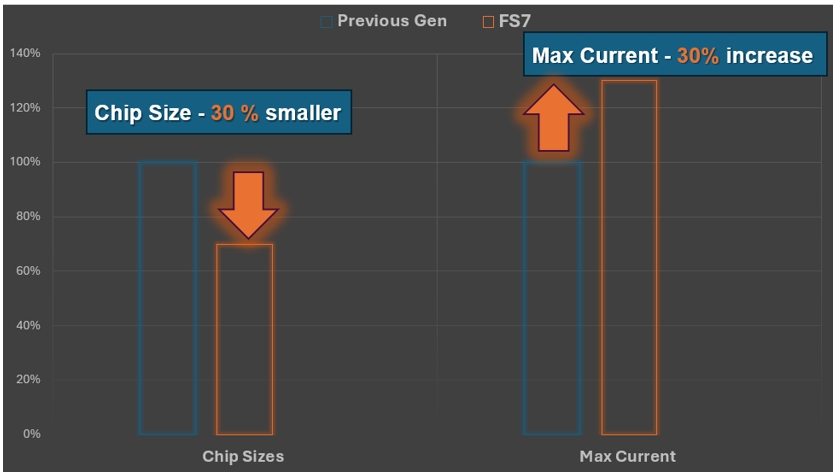
At present, if 600 A IGBT modules are used in the ANPC/INPC architecture to design a 1.725MW inverter, a total of 36 modules will be required. However, if the new NXH800H120L7QDSG and SNXH800H120L7QDSG with A rated operating current of 800 A are used, the number of modules required for the design will be reduced by 9. Accordingly, the size, weight and cost of the design will be saved by 25%. This is very valuable for both solar and CAV applications, as the weight reduction and increased efficiency will lead to an increase in vehicle mileage.

All of On's QDual3 modules undergo rigorous reliability testing that exceeds the reliability of other comparable devices on the market. Our humidity tests require products to withstand a 960V bias for up to 2,000 hours, while comparable devices only need to withstand an 80V bias for 1,000 hours. Vibration testing is critical for CAV applications and our products are tested for up to 22 hours at 30 G peak /10G RMS to meet AQG324 requirements. Other devices are tested at vibration levels as low as 5 G, with durations as short as 1 hour.
Sum up
The use of renewable energy around the world is increasing and the power grid is under tremendous pressure. Solar power has matured and will surpass wind power as the main source of renewable electricity by 2022.
Although fossil fuel-powered vehicles are still a major source of pollution, the electrification of CAVs is progressing steadily and is beginning to pay off.
New semiconductor technologies such as ON Semiconductor FS7 enable the development of low-loss, high-power devices to meet the efficiency and reliability needs of these areas. Based on this technology, On's new QDual3 devices are packaged in a compact package that enables high power density and excellent energy efficiency. Well-welded terminals and certified testing that exceeds others in the industry help ensure robust performance for QDual3 devices.
Thanks to the new NXH800H120L7QDSG and SNXH800H120L7QDSG modules with current capabilities up to 800 A, inverter design requires 25% fewer modules and can further simplify the design, reduce its size, mass and cost.
This is undoubtedly a significant development, and ON will continue to explore the high performance potential of FS7 technology and strive to introduce more modules that go beyond existing standards to meet the growing needs of the solar industry and CAV manufacturers.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


