There are two basic types of AC motors: single-phase and three-phase. Generally speaking, single-phase AC motors are typically used in residential applications such as household appliances, while three-phase AC motors are employed in industrial applications. This is mainly because most households use single-phase power supplies, while most industrial sites use three-phase power supplies.
Given these two different power supply schemes, which motors can be used in what situations? What will happen if the motor is used incorrectly or if there is a faulty power supply? This article will explore some of these options.
Single-phase power supply and three-phase power supply
Before discussing the motor itself, it is very important to understand the meanings of "single-phase" and "three-phase" power supplies. Single-phase power supply is a commonly used power source in many households. It is a standard wiring method with three wires: two live wires (or one live wire and one neutral wire) form a circuit and transmit current under normal circumstances, while a ground wire only transmits current to the ground in case of a fault to ensure safety. In the United States, the voltages between these wiring schemes are 240 V or 120 V RMS respectively, and the oscillation frequencies are all 60 Hz.
A three-phase power supply can have four or five wires, depending on the configuration. There are three phase lines, sometimes a neutral line, and almost always a ground line (the ground line is usually not installed as one of the wires, so it may be "three wires..."). Or "Four wires with a ground wire"). The three phase lines each act as live wires, but their phases differ by 120 degrees from each other.
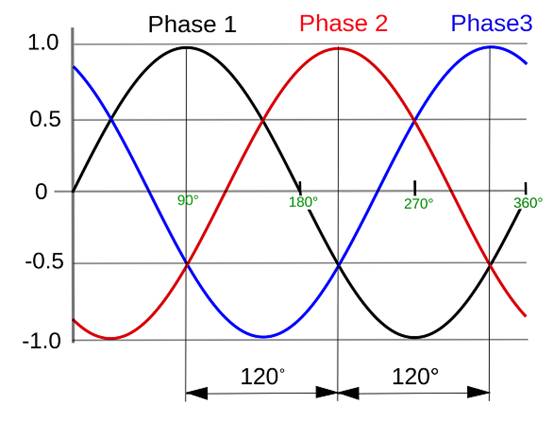
Three-phase AC motors have some unique advantages. Specifically, the speed can be strictly controlled by using a variable frequency drive (VFD) with pulse width modulation (PWM), while most single-phase motors have only a few taps and can only achieve a few fixed speeds. In addition to speed control, three-phase AC motors can operate more efficiently, providing higher and more stable power, and can run at higher voltages to consume less current.
Can a single-phase motor operate with three-phase electricity?
If a three-phase system is equipped with a neutral line, for instance, a 208-volt power supply in a star configuration, where the voltage from the line to ground is 120 volts, then it is actually a true single-phase power supply, and we have no problem with this motor at all! The problem to be solved here is whether a single-phase motor can be connected to a three-phase power line if there is no neutral line in the power supply.
Although not ideal, as long as the voltage between the lines does not exceed the rated value of the motor, a single-phase motor can work together with a three-phase power supply system. However, a common misunderstanding must be avoided. It is very easy for people to connect the motor to the single phase of the three-phase system. The problem with this configuration lies in the three-phase imbalance.
Theoretically, three single-phase motors can be connected to each phase of a three-phase system as long as they are similar enough to minimize the load differences among the three phases. This is called a "three-phase motor unit", and it is used for some tasks of HVAC, robotics and material transportation types. Consider an assembly line where multiple motors may rotate at the same speed, with consistent loads that are not extreme. In this case, the three-phase motor set can be balanced relatively easily.
Since single-phase motors are typically designed for a power supply of 120 V/60 Hz, it is crucial to ensure that the motor can handle any frequency control provided by the VFD, but most motors are unable to do so. The separate speed control among the three phases to maintain this balance is also very tricky. In addition, uneven wear or load will increase the imbalance between phases, which not only affects the service life of the motor but also reduces the efficiency of the system. In conclusion, in most cases, using a three-phase motor is much better (and cheaper) than trying to use three single-phase motors.
The wiring of the three-phase motor is incorrect
One potential problem with three-phase power supply is that one or more phases may fail. It is entirely possible that one phase malfunctions and the power supply is no longer available. If a three-phase motor only operates on a two-phase line (whether due to a fault or because the motor is running on a single-phase power supply), all the advantages of using a three-phase motor will disappear.
Speed control is much more difficult because at least one phase is missing, which means the remaining phase must make up for the difference. The frequency converter must adjust the missing phase. If it can be adjusted through a speed sensor, it may only increase the current consumption of the remaining phase, physical and thermal overload, and a series of related problems. If the frequency converter is only used as the output end, it will not accurately adjust the motor to the appropriate speed. Furthermore, even if the current consumption is high, the motor will operate at a lower torque, which means that the overall efficiency is reduced and it may be difficult to start or run.
Furthermore, the motor is no longer in an electrical or magnetic equilibrium state, which will generate electromagnetic interference (EMI). Some of these signals will be suppressed by the chassis, but EMI may affect nearby instruments. Imbalance is not only electrical but also mechanical. Vibration can be detected on the motor load.
Overall, if the phase connection of a three-phase motor is incorrect, it will cause the motor to generate electrical noise, imbalance, and its performance and efficiency will decrease. The motor is more prone to overload and its service life may be shortened.
It is worth noting that VFD can do many things, so it can be used to simulate a three-phase system. By appropriately adjusting the VFD, unbalance and vibration can be reduced, while the torque and speed can approach those during three-phase operation.
There is another wiring scheme, that is, placing a large capacitor between the terminals to shift the signal phase. The appropriate capacitor size (and the appropriate time constant) can cause sufficient phase shift to simulate three phases.
Frequency: 60 Hz vs. 50 Hz
Although the standard in the United States is 60 Hz, most parts of the world use 50 Hz power supplies. Suppose a company wants to establish a dual manufacturing plant overseas that matches the existing factory in the United States. If the same motor is used, the running speed of a 50 Hz motor will be slightly slower, it will consume more current, and the torque will also be lower than expected.
The motor will operate, but this is not a factor to be considered. Usually, the cooling fan of the motor is connected to the same shaft as the motor. If the motor speed slows down, the fan speed will also slow down and the cooling effect will be reduced. The reduction in cooling capacity combined with the increase in current consumption will greatly increase the possibility of thermal overload. The motor is designed to operate at a specific working frequency, so it is very easy to find the right motor for the appropriate power supply system.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


