Fixed resistor refers to the resistor whose resistance value is fixed and unchanged after production. Figure 1-1 shows the physical appearance and circuit symbols of the fixed resistor.

Buck current limiting, shunt and partial voltage function description
The main functions of the resistor are buck current limiting, shunt and partial voltage. Figure 1-2 shows the functions of the resistor such as buck current limiting, shunt, and voltage dividing.
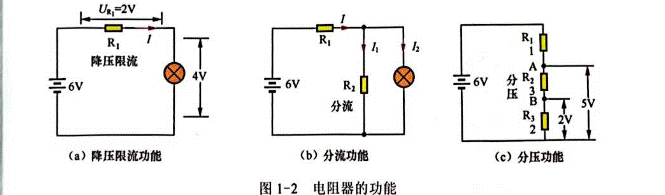
In the circuit shown in Figure 1-2 (a), resistor R1 is connected to the bulb in series. If a wire is used to directly replace R1, the voltage added to the third end of the bulb will be 6V, and the current flowing through the bulb will be very bright. After the series resistor R1, the voltage at both ends of the bulb will be reduced to 4V due to the 2V voltage on R1, and the voltage at both ends of the bulb will be reduced to 4V. The current flowing through the pack is reduced. The resistor R1 here plays a role in reducing voltage and limiting current.
In the circuit shown in Figure 1-2 (b), the resistor R2 is in parallel with the bulb, and the current flowing through R1 not only passes through the bulb, but also flows back to the power supply through R2, thus reducing the current flowing through the bulb and dimming the bulb. This function of the electric l unit R2 is called shunt.
In Figure 1-2 (c) circuit, resistors R1, R2 and R3 are connected in series, starting from the positive terminal of the power supply, the voltage will be reduced after each resistor, the voltage reduction depends on the size of the resistor resistance value, the greater the resistance value, the more the voltage reduction, R1, R2 and R3 in Figure 1-2 (c) will divide the 6V voltage into 5V and 2V voltage.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


