In order to achieve the bidirectional flow of current, back-to-back series MOSFETs are usually used to form a bidirectional switch. This paper will analyze the working principle of back-to-back MOSFETs and discuss their application in bidirectional current control.
Ⅰ、Dual pilot principle of back-to-back series MOSFETs
The MOSFET is essentially a single-pass switch, and the current between the source and drain can only flow along the "drain → source" direction, while the body diode determines its reverse characteristics. In order to realize dual conduction and bidirectional blocking, it is necessary to use two MOSFETs back-to-back in series to build a complete bidirectional switch.
The basic structure of back-to-back series MOSFETs is as follows:
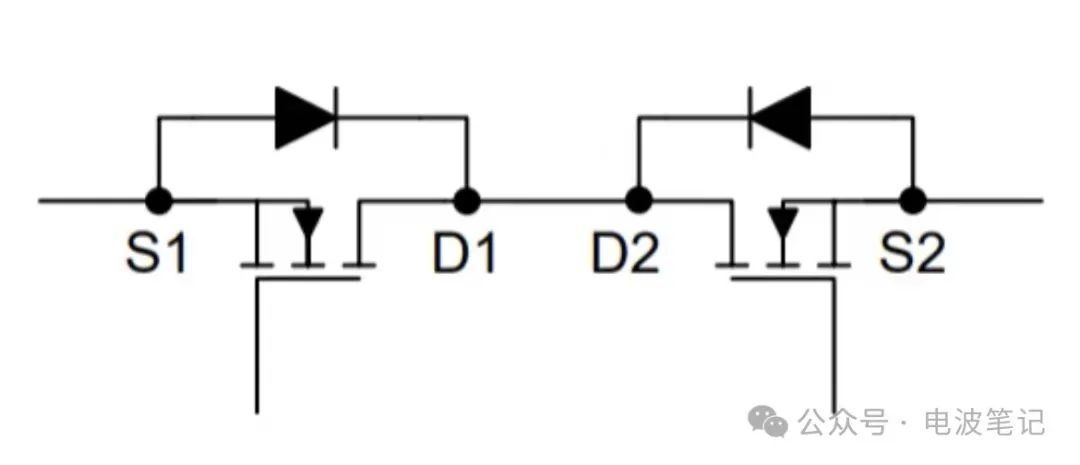
Among them, the Drain or Source of the two MOSFETs are connected to form a symmetrical bidirectional switching structure. Depending on the connection method, common back-to-back MOSFET topologies come in two forms:
Common Drain structure:
The sources are connected to the input and output terminals respectively, and the drains are connected to each other.
Applicable to high-voltage blocking scenarios.
Common Source structure:
The drains are connected to the input and output terminals respectively, and the sources are connected to each other.
Suitable for low voltage high frequency switching applications.
The working mechanism of double wizard pass
In dual pilot mode, both MOSFETs need to be on to allow current to flow in either direction. Let the two MOSFETs be Q1 and Q2 respectively, and the gate control signals are G1 and G2. When the gate of two MOSFETs simultaneously applies a sufficient drive voltage (Vgs > Vth, usually more than 10V), both enter the on-state to achieve bidirectional conduction.
Forward current (left to right) : The drain → source of MOSFET Q1 is on, while the body diode of Q2 is also on, allowing the current to flow.
Reverse current (from right to left) : the drain → source of MOSFET Q2 is on, while the body diode of Q1 is on, and the current direction is opposite to the forward direction.
The working mechanism of bidirectional blocking
When the gate signals of both MOSFETs are low (Vgs < Vth), the MOSFETs enter the off state. Since the body diodes of the two MOSFETs are in opposite directions, the current in any direction cannot be conducted, resulting in a two-way blocking state.
In this way, the voltage in both positive and negative directions can be blocked at the same time when turned off, improving the safety of the system.
Ⅱ、Typical applications of back-to-back MOSFETs
2.1AC switching circuit
In AC power control applications, since the current is an AC signal, a switch capable of controlling two-way current is required. Therefore, the traditional one-way MOSFETs can not be directly used for AC switching, and back-to-back series MOSFETs can effectively realize the switching control of AC current. For example:
Solid-state relays (SSRS) : Use back-to-back MOSFETs for contactless electronic switching to improve switching life and reliability.
Ac Voltage regulator: Used to regulate AC load voltage, such as LED drives and smart grid systems.
2.2Battery Management System (BMS)
In a battery protection circuit, current may flow in both directions. For example, in charging mode, current flows from the charger to the battery; In discharge mode, the current flows from the battery to the load.
Back-to-back MOSFETs are used for charge and discharge control to ensure complete isolation of charge and discharge paths and avoid safety issues caused by reverse charging.
2.3 Bidirectional DC-DC Converter
In new energy systems (such as electric vehicles, photovoltaic energy storage systems), two-way DC-DC converters need to switch between charge and discharge, and back-to-back MOSFETs can effectively control two-way energy flow and improve system energy efficiency. For example:
Electric vehicle charging and discharging: when the vehicle is charging, the current flows to the battery; In V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) mode, the battery current needs to flow back to the grid, and back-to-back MOSFETs can achieve efficient bidirectional conversion.
Back-to-back series MOSFET is an efficient bidirectional switching scheme, which is widely used in AC control, battery management, bidirectional DC-DC converter and other fields. The basic principle is to use the symmetrical structure of the two MOSFETs, so that it can reduce the loss when the double pilot is on, and completely block the current when the switch off, so as to achieve efficient and safe bidirectional control.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


