Resistors are basic and commonly used in all electronic components, they play a vital role in the circuit, different types of resistors, their accuracy is not used, stability, high voltage, high current is also different.
But their common characteristics are: temperature coefficient, voltage coefficient, noise, frequency response, power and resistor temperature rating, physical size and reliability.
Fixed resistors have only one resistance value, 100Ω. But variable resistors (potentiometers) can provide an unlimited number of resistance values between zero and value.
Let's look at the standard resistance symbols
Carbon resistors are common combination resistors and are an inexpensive general-purpose resistor used in electrical and electronic circuits. Their resistive elements are made from a mixture of finely ground toner or graphite (similar to pencil lead) and non-conductive ceramic (clay) powder that bonds them together.
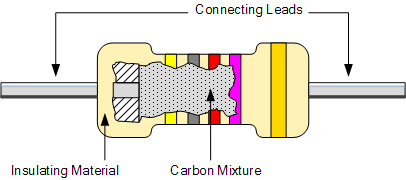
The higher the proportion of carbon, the lower the total resistance. It is a low to medium power resistor suitable for high frequency applications, but at high temperature conditions, it is affected by noise and stability. Their symbol is "CR".
Thin film type resistor
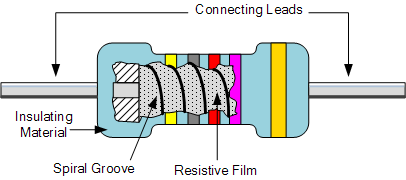
Metal film, carbon film and metal oxide film resistor types, the resistance value of the resistor is controlled by increasing the desired thickness of the deposited film, so they are called "thick film resistors" or "thin film resistors".
They compare carbon composition types, such manufacturing methods are closer to resistors with tolerances (1% or less), and thin-film resistors also have higher ohms than other types and values in excess of 10 Mω (10 million ohms).
Metal film resistor
Metal film resistors have better temperature stability than carbon equivalents, lower noise, and are generally better suited for high frequency or RF applications. Metal film resistors are available in E24 (±5% and ±2% tolerances), E96 (±1% tolerances) and E192 (±0.5%, ±0.25% and ±0.1% tolerances) packages with power ratings of 0.05 (1/20) watts up to 1/2 watt.
Metal oxide resistors have better high surge current capabilities and have much higher temperature ratings than equivalent metal film resistors.
Thick film resistors are another type of thin film resistors that are made by depositing thicker conductive slurries. They have good temperature stability, low noise and good voltage rating, but low inrush current characteristics.
Wire wound resistors are made by winding a fine metal alloy wire (nickel-chromium alloy) or similar wire to an insulating ceramic shaper in a spiral form similar to the film resistors described above.
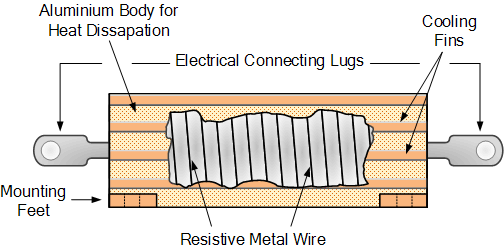
These resistors have very low ohmic precision values (from 0.01Ω to 100 kω), and they are generally suitable for applications such as measurement circuits. They are also capable of handling much higher currents than other resistors of the same ohm value with a rated power of more than 300 watts.
Power wire-wound resistors These are high temperature, high power non-inductive resistors types, usually coated with glass or glass epoxy enamel,
One of the main uses of power wire-wound resistors is an electric heating element for electric fire, which converts the current flowing through it into heat, dissipating up to 1,000 watts, (1kW) of energy per element. Wire-wound resistor types are prefixed with the "WH" or "W" symbol (e.g. WH10Ω).
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


