Should I use a linear charger or a switch charger?
Linear and switching chargers are used in a wide range of applications: hearing AIDS, smartwatches, sensor nodes, mobile phones, laptops... There are too many! Whenever you use a rechargeable battery, you need a charger. However, given the pros and cons associated with the different charging topologies available, you may need to consider more factors when choosing a charger.
Each approach has its pros and cons. The linear charger is small in size, easy to use and low in cost. They are suitable for noise sensitive applications without any switching; However, when the charging current is large, the power consumption is high. Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of a linear charger.
Switching chargers are known for their high efficiency and minimize power consumption across a wide range of input adapter voltages. However, compared with linear chargers, additional inductors and capacitors consume more board space, increasing BOM costs and design complexity. Figure 2 shows the diagram of the switch charger. Table 1 compares the functions of the two charger types.
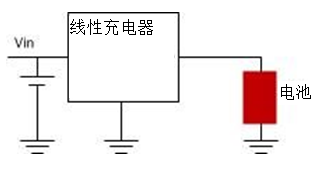
Figure 1: Linear charger diagram
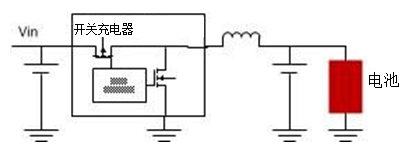
Figure 2: Switch charger diagram
| Linear charger | Switch charger |
| Large power consumption, large charging current | Higher efficiency and lower power consumption |
| Simple design; Small solution size | More complex design |
| Reduce cost | More components; Bengaard |
| No electromagnetic interference (EMI) issues | Switching noise may require more layout consideration |
| Suitable for charging small batteries or batteries with <1.5A charging current | Suitable for large capacity batteries and fast charging |
Table 1: Comparison of characteristics of linear chargers and switch chargers
These charger products are customized to support different battery chemicals such as lithium ion, lithium polymer, LiFePO4, NiMH, lead acid, etc. Due to their high energy density, low maintenance frequency, and low self-discharge characteristics, lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in consumer and industrial applications. Due to their stability and reliability characteristics, LiFePO4 and NiMH are often found in automotive applications.
The next time you consider a linear or switching battery charger and optimize your application, consider this guide. Happy design!
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


