What is a motor?
In a broad sense, "motor (mortor)" is a power device, such as motorsport and other car-related English terms will also be used, here the "motor" refers to the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy "motor".
So how does an electric motor (motor) convert electrical energy into mechanical energy?
A motor uses electrical energy to form electromagnets, and uses the interaction of magnets (gravitational and repulsive forces) to produce mechanical energy.
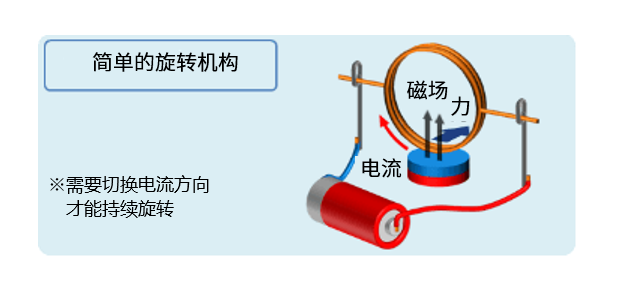
There is another explanation, perhaps this explanation is more general, it can also be said that the motor "uses the force of the energized conductor in the magnetic field." This involves "Fleming's left hand rule". We can use the simple rotating mechanism diagram below to understand this principle in detail (note: the current direction needs to be switched in order to continue to rotate). However, its structure is slightly different from the actual motor structure that will be introduced later, so here I will first roughly explain the "application of electromagnets".
Electromagnets are made by winding wires around a magnetic material such as iron. Of course, nothing happens just by winding, but when the current flows through the wire, the magnetic material will have the properties of a magnet and will attract other magnets (iron, etc.). In addition, since the magnetic poles can be changed by changing the direction of the current, if another magnet is configured opposite one magnet, the force applied to that magnet can switch between the gravitational and repulsive forces (see figure below).
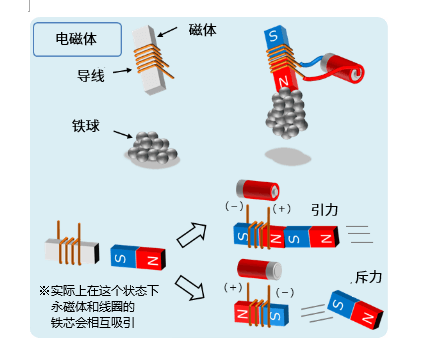
The so-called motor is based on this electromagnetic characteristic and uses electrical energy to achieve rotational motion (note: there are also linear motors and other motors that do linear motion).
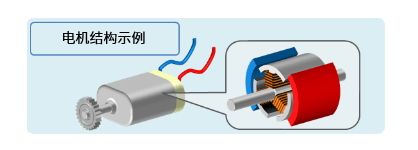
Now that you know that mechanical energy is obtained through the attraction and repulsion forces of magnets, how is continuous rotational motion achieved? It is easy to understand this point by looking at the structure of motors used in works such as wireless remote control cars and electronic manufacturing. The "motor" of mechanical energy.
The rotation principle of the motor
Let's take the basic brush motor as an example to understand the rotation principle of the motor.
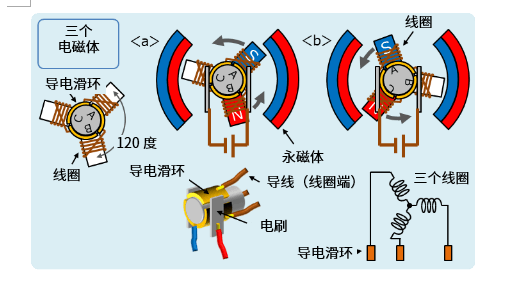
In order to facilitate everyone to understand why this 120 degree Angle structure, we first use a diagram of the electromagnet to explain its rotation principle.
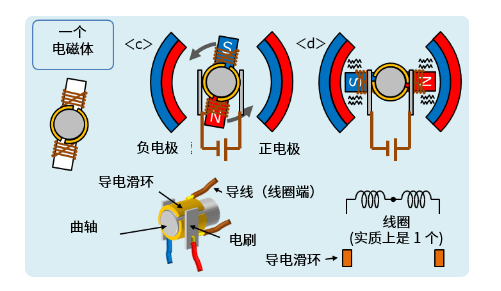
Based on this structure, for example, when there is a coil in the figure, the position of the conductive slip ring is adjusted to make the current flow, so that the magnetic pole of the electromagnet becomes the magnetic pole as shown in the figure. In this way, a counterclockwise force is generated in the coil, which enables the motor to rotate.
Next, let's look at what happens when the coil is rotated to reach its position. At this position, if the polarity of the magnet remains the same, then the coil will stop, so the polarity of the magnet needs to be changed at this position. Fine-tune the position of the conductive slip ring so that the connection between the brush and the slip ring is reversed at this position, so that the motor can maintain continuous rotation.
However, if you look closely, you will notice the difficulty of this structure. For example, it is actually very difficult to switch the electrodes in the position at the right time, and if there is a problem with the electrode switching here, the motor will stop running. In addition, the contact between a conductive slip ring and two brushes can cause a short circuit between the positive and negative electrodes, which can cause a failure.
To solve these problems, designers came up with a structure that uses three coils and places the electromagnets at 120-degree intervals. A motor of this structure is called a "three-phase motor", and the motor in the example is such a motor. By the way, a motor consisting of an electromagnet is called a "single-phase motor."
The "three electromagnets" diagram above is a schematic diagram of the three-phase motor structure. There are three coils, one end of each coil is connected to the conductive slip ring, and the other end connects the three coils. In this connection, a voltage is applied to the two conductive slip rings with a brush, so that the two coils are magnetized. In this way, for example, coils A and B are magnetized at position, coil B, which becomes the N pole at position, is demagnetized, and coil C becomes the N pole. If this were the case, the situation in the "one electromagnet" diagram would not occur. Moreover, with this conductive slip ring configuration, there is no short circuit between the positive and negative electrodes.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


