PWM frequency: refers to the number of times a signal goes from a high level to a low level and back to a high level in a second, that is, how many cycles a second PWM has.
If the frequency is 50Hz, that is, one cycle is 20ms, then there are 50 PWM cycles per second.
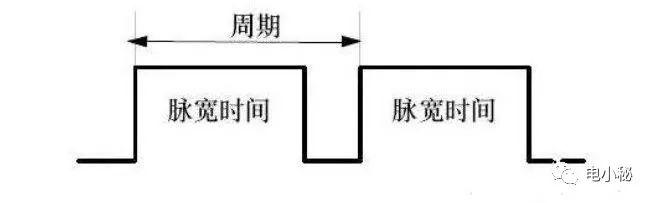
Duty cycle: is the ratio of the time of the high level to the entire cycle time in a pulse period.
Period: The time of a pulse signal, and the number of 1s internal test periods is equal to the frequency.
Pulse width time: high level time.
The ratio of pulse width time to total cycle time in the figure above is the duty cycle ratio.
The basic principle of PWM control
When the narrow pulses with equal impulse but different shape are added to the link with inertia, the effect is basically the same. Impulse refers to the area of a narrow pulse. The effect is basically the same, which means that the output response waveform of the link is basically the same. The low bands are very close, with only slight differences in the high bands.
The frequency of pwm refers to the number of times per second that the signal goes from high to low and back to high, and the duty cycle is the ratio between the high and low level duration.
The higher the frequency of the pwm, the faster it will respond to the output, and the lower the frequency, the slower the output response.
The regulating effect of pwm comes from the width control of the "occupy period", the "occupy period" becomes wider, the output energy will be increased, the average voltage obtained by the resistance and capacitance transformation circuit will also rise, the "occupy period" narges, the output energy will be reduced, the average voltage obtained by the resistance and capacitance transformation circuit will also decline. pwm is through this principle to achieve D/A conversion.
The relationship between PWM duty cycle, frequency and period
Frequency refers to the period, and the frequency is reciprocal with the period. Pulse width and duty cycle are related to the period. The pulse width is the time occupied by the high level in a cycle, and the duty cycle (as its name indicates) is the proportion of the high level in a cycle. For example, if the frequency is F and the duty cycle is P, then the pulse width = (1/F) *P.
Relationship between pwm duty cycle and output voltage
The PWM part makes the average voltage reach the stable voltage value through the duty ratio regulation, but the real output stable voltage is a filter composed of inductance and capacitance after PWM. The inductor turns the discontinuous voltage into a relatively stable current, and the capacitor turns the current into a relatively stable voltage.
If it is connected to a DC motor, it does not need capacitance at all, as long as the stable current reaches the purpose, the equivalent voltage is the average voltage.
Using a low-pass filter can lead to a smoother voltage, but not too smooth because your PWM frequency is too low. A low-pass filter composed of resistive capacitors can be used to select a break frequency of 30Hz. The problem with this is that you do get a smooth output, but the frequency does not exceed 30Hz.
The duty cycle of PWM determines the average voltage output to the DC motor.
PWM does not regulate current. PWM means pulse width regulation, which is to adjust the time ratio of square wave high level and low level
A 20% duty cycle waveform will have 20% high level time and 80% low level time,

Relation between Pwm duty cycle and output current
The larger the pwm duty cycle, the power tube turn-on time will increase, the larger the output power, the larger the current, the larger the charging current, in theory.
PWM current wave: current-type inverter circuit for PWM control, the resulting PWM current wave.
WM waveform can be equivalent to various waveforms:
Dc chopper circuit: equivalent DC waveform
SPWM wave: equivalent sinusoidal waveform, can also be equivalent to other required waveform, such as equivalent required non-sinusoidal AC waveform, its basic principle and SPWM control is the same, also based on the equivalent area principle.
With the development of electronic technology, a variety of PWM technologies have appeared, including: phase voltage control PWM, pulse width PWM, random PWM, SPWM, line voltage control PWM and so on.
The output voltage and current, and through the PWM drive output to change the size of the voltage and current, through the collected voltage and current and the target voltage and current are compared, want to increase the output voltage and current to increase the PWM output duty ratio, reduce the output voltage and current to reduce the PWM output duty ratio.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


