DC-DC circuit principle:
Dc-dc is an abbreviation of English DC to DC, so a DC-DC circuit is a circuit that converts a DC power supply into a different voltage value. DC-DC is a branch of switching power supply technology, including AC-DC, DC-DC two branches. DC-DC circuits are divided into:
Boost converter: A circuit that converts low voltage to high voltage.
Buck converter: A circuit that converts high voltage to low voltage.
Inverter: The circuit that changes the voltage polarity, there are two types of positive power supply to negative power supply and negative power supply to positive power supply.
The three main branches, of course, when applied in the same circuit will have boost reverse, buck boost and other functions exist at the same time.
The basic circuit of DC-DC converter has three kinds: boost converter, buck converter and lift converter.
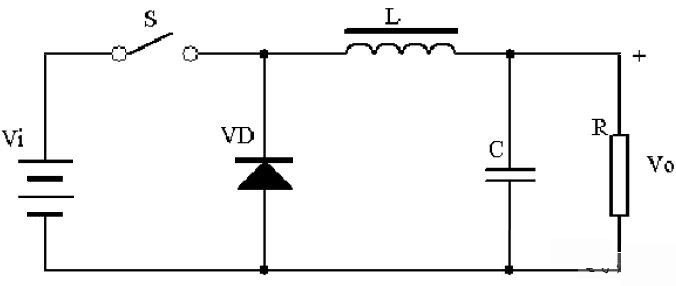
As shown in Figure 1, when the switch is closed, the voltage at both ends of the inductor is (Vi-Vo), and the inductor is excited by the voltage (Vi-Vo), and the magnetic flux increased by the inductor is (Vi-Vo)*Ton.
When the switch is turned off, due to the continuity of the output current, the diode VD becomes on, the inductance is magnetized, and the magnetic flux reduced by the inductance is: (Vo)*Toff.
When the state of switch on and switch off reaches a balance, (vi-vo)*Ton=(Vo)*Toff, because the duty cycle D<1, so Vi>Vo, to achieve the voltage reduction function.
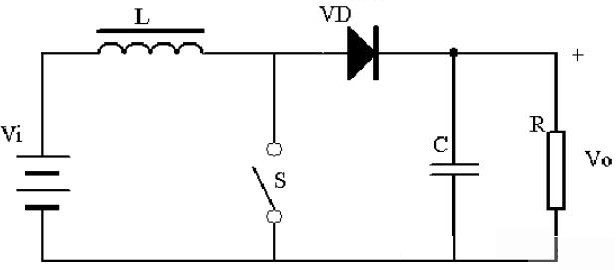
When the switch is turned off, due to the continuous output current, the diode VD becomes on, the inductance is magnetized, and the magnetic flux reduced by the inductance is: (Vo-Vi)*Toff.
(Vi)*Ton=(Vo-Vi)*Toff when the state of the switch on and off is in equilibrium, because the duty cycle D<1, Vi.
As shown in Figure 3, when the switch is closed, the inductance is excited by voltage (Vi), and the magnetic flux increased by inductance is: (Vi)*Ton; When the switch is turned off, the inductance is magnetized, and the magnetic flux reduced by the inductance is: (Vo)*Toff. When the state of the switch on and off reaches a balance, the increased flux is equal to the reduced flux, (Vi)*Ton=(Vo)*Toff, depending on the Ton ratio Toff value, Vi< Vo, or Vi>Vo.
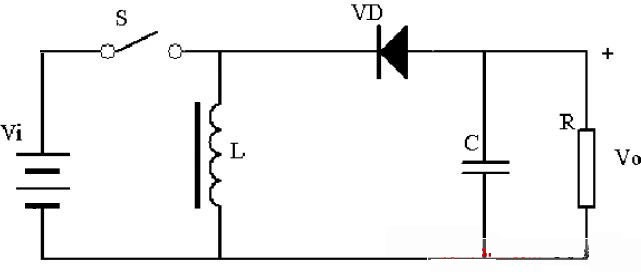
FIG. 3 Schematic diagram of the lift converter


