
Class D power amplifiers are compact in size, low in heat generation, high in efficiency, low in energy consumption, light in weight, and their technology is becoming increasingly mature.
Many friends have asked me whether a D-class amplifier is considered a digital power amplifier.
From a technical logic perspective, it is calculated.
The core technology in Class D power amplifiers is PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) technology. Its relationship with "digital" is mainly reflected in the signal processing method and implementation logic, which can be understood from the following perspectives:
1. The essence of PWM is "the digital expression of analog signals".
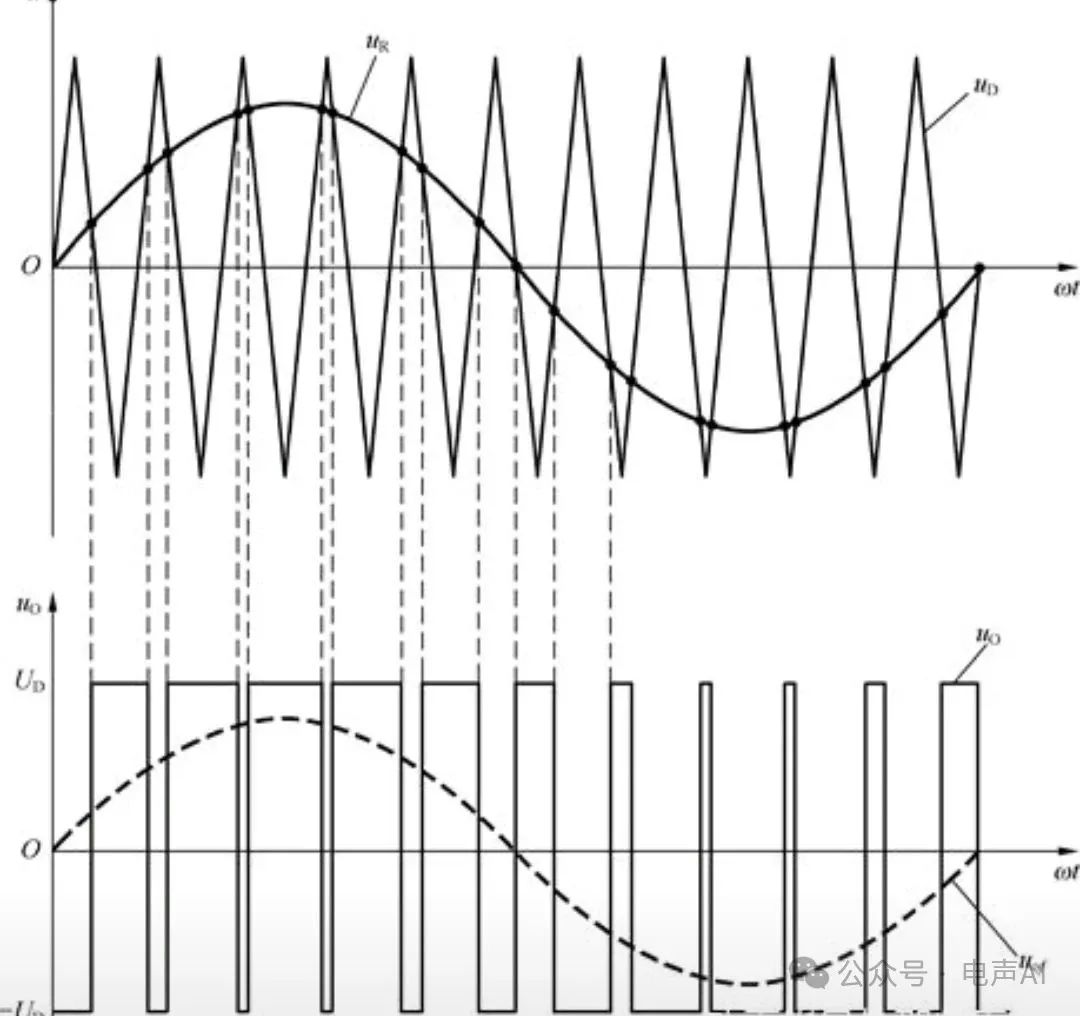
The PWM waveform seems to be a square wave (alternating high and low levels), but the variation of its pulse width strictly corresponds to the amplitude of the analog input signal:
The input analog audio signal (such as a sine wave) is converted into a series of pulses, and the pulse width varies in real time with the strength of the analog signal (a strong signal leads to a wide pulse, while a weak signal results in a narrow pulse).
This approach of "representing continuous analog signals with the width of discrete pulses" is essentially a digital coding process - achieving quantitative expression of analog signals through digital logic (such as comparators and timers).
2. Digital circuits are the core implementation carriers of PWM
The generation and control of PWM signals almost entirely rely on digital circuits:
When generating PWM, the analog input signal needs to be compared with a high-frequency triangular wave (or sawtooth wave) through a comparator to output a square wave with varying pulse width. During this process, the generation of triangular waves, the logical judgment of comparators, etc., can all be achieved through digital chips (such as MCUS, dedicated PWM controllers).
Compared with traditional analog power amplifiers (such as Class A and Class B) that rely on the linear amplification of transistors, the core of Class D power amplifiers is "digital switch control" (transistors operate in a switching state and only output high and low levels), and its control logic belongs to the digital category.
3.The difference from "pure digital signals"
It should be noted that the PWM waveform itself is not a "pure digital signal" (such as binary code), but an analog pulse waveform under digital control:
Pure digital signals (such as I²S audio signals) are discrete binary data, while PWM is a continuously changing sequence of pulses, and its information is carried in the analog variation of pulse width.
However, since the generation and processing of PWM rely on digital logic and ultimately transfer energy through switching states (0/1 levels), it is often classified under the category of "digital power amplifiers".
In summary, the PWM of Class D power amplifiers encodes analog signals through digital logic and is the product of digital processing of analog signals. Its core control logic and implementation methods are closely related to digital technology.
So, referring to Class D power amplifiers as digital power amplifiers, although not rigorous in technical logic, is not a big mistake.
Besides, over the years, the industry has become accustomed to referring to Class d power amplifiers as digital power amplifiers, and this has become a common practice.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


