The principle of the frequently used DC motor is electromagnetization: the energized wire will produce a magnetic field. That's electromagnetically induced rotation and the magnetic field drives the rotor.
The motor is composed of a stator and a rotor, one generates a rotating magnetic field, one is a magnetic pole, and the rotor (bearing) of the motor turns up.
This achieves the conversion of electrical energy -> magnetic energy -> mechanical energy.
The following diagram can be more intuitive to understand:
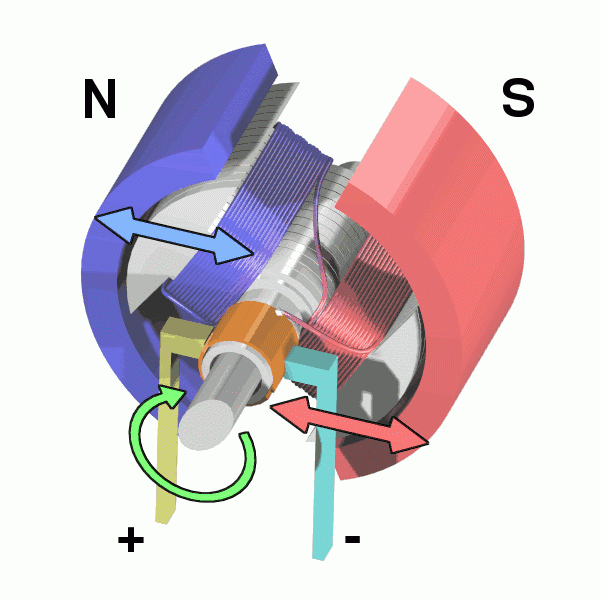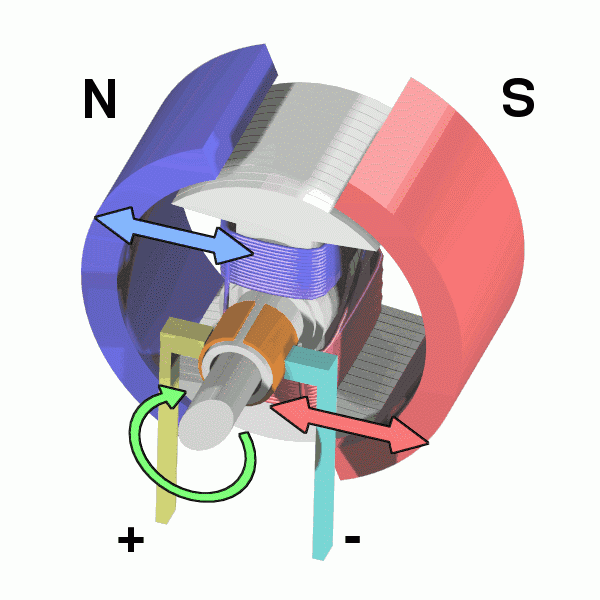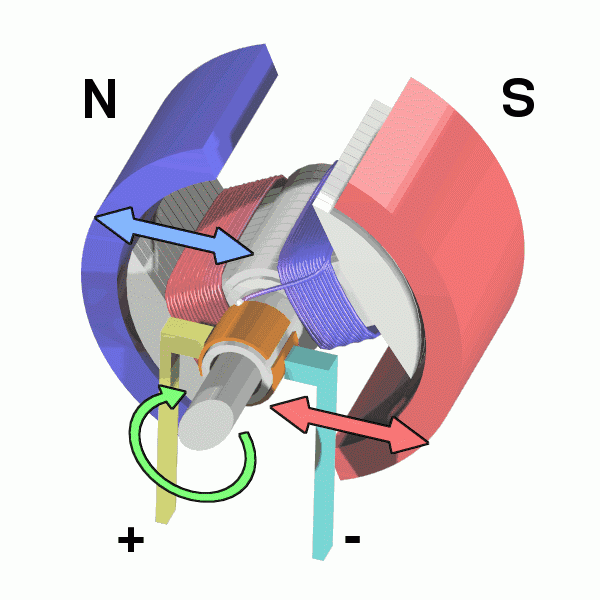
PWM principle
PWM control motor speed, in fact, is to control the size of the power supply current to achieve.
The force on an energized wire in a magnetic field is called the ampere-force, and the formula for the ampere-force is F=BIL.
Where F is the force, I is the current, and L is the length of the wire. Under the condition that other conditions remain unchanged, controlling the current through it is to control the size of the amperage force.
The resistance R of the motor is basically constant, then the current I = U/R, F= BLU/R.
In the case of constant R, B and L, controlling the size of the amperage force is essentially to modify the size of the supply voltage.
We also know that the essence of controlling the motor speed is to provide different power supply voltages to the motor, and the greater the voltage, the faster the motor speed.
The essence of PWM is pulse width modulation, through the output of different duty ratios, so as to convert DC voltage into analog signals with different voltage values.
Control motor speed
Duty cycle can achieve the adjustment of motor speed, we know that duty cycle is the ratio of high level in a cycle, the higher the ratio of high level, the greater the duty cycle, for DC motor, motor output pin is high level motor can rotate, when the output high level, the motor will rotate, but it is a little bit of speed up. When the high level suddenly turns to the low level, the motor will not stop due to the effect of inductance to prevent current mutation, and will maintain the original speed, so as to reciprocate, the speed of the motor is the average voltage value of the output during the cycle, so in essence, we speed regulation is to put the motor in a state, like stop not stop, like full speed rotation and not full speed rotation. So the average velocity over a period is the velocity that our duty cycle determines.
Sum up
In the motor control, the higher the voltage, the faster the motor speed, and through the PWM output of different analog voltage, you can make the motor to achieve different output speed.
Of course, in motor control, different motors have their own adaptive frequency, too low frequency will lead to unstable movement, if the frequency is just in the range of human ear hearing, sometimes you will hear whistling. The motor with too high a frequency may not react, and the normal motor frequency is between 6-16kHZ.
The output voltage is different, and the motor speed is different. Then we can know that the speed regulation of the motor can be achieved by sliding rheostat or replacing the power supply of different voltages, but in practical applications, PWM is obviously more convenient.
A more professional word is:
The so-called PWM is the pulse width modulator, through the modulator to provide a motor with a certain frequency of pulse width adjustable pulse electricity. The greater the pulse width, the greater the duty cycle, the greater the average voltage provided to the motor, and the higher the motor speed. On the contrary, the smaller the pulse width, the smaller the duty cycle. The lower the average voltage supplied to the motor, the lower the motor speed.
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


