One of the topics I saw shared during DesignCon was "Why 48V power successfully replaced 12V power". I had planned to listen, but it conflicted with another topic, so I missed it
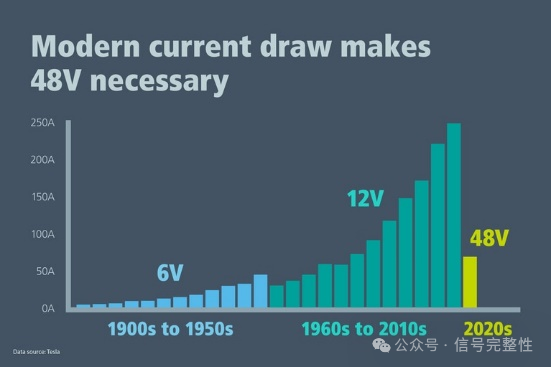
The gradual increase in voltage has a long history, and 48V replacing 12V has had some success in many areas, mainly because it has obvious advantages in terms of energy efficiency, power and system design. Here are the key reasons:
1. Reduce wire loss and improve energy efficiency
The loss in power transmission is mainly determined by the resistance loss (I²R) caused by the current. With the same power transmission requirements, increasing the voltage can reduce the current and thus reduce the power loss. For example:
•°P = U × I,For the same power demand, increasing the voltage can reduce the current.
•Line loss P_loss = I² × R, current is reduced by 4 times, loss is reduced by 16 times (48V compared to 12V)。
As a result, 48V systems can significantly improve power supply efficiency, reduce copper losses, and reduce wiring costs。
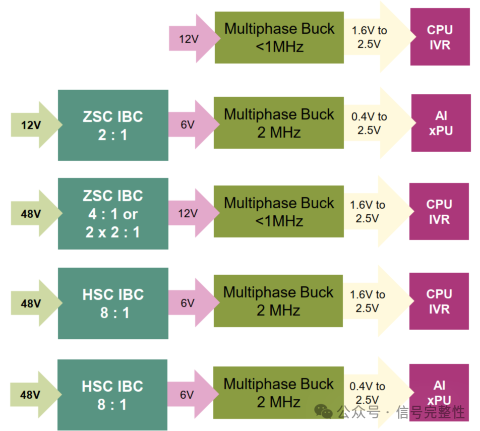
2. Higher power density to support higher power loads
•When the 12V power supply system is used in high power applications (>1kW), it needs to carry a large current (such as more than 100A), resulting in complex wiring and increased loss.
•48V systems can transmit the same amount of power at lower currents, making the power supply design more compact and lightweight, especially for high-power applications such as servers, data centers, and EV (electric vehicle).
•Companies such as Google, Meta (Facebook), and Amazon have adopted 48V power architectures to optimize data center energy efficiency.
•The Open Compute Project (OCP) is also promoting 48V server architecture as an alternative to the traditional 12V solution.
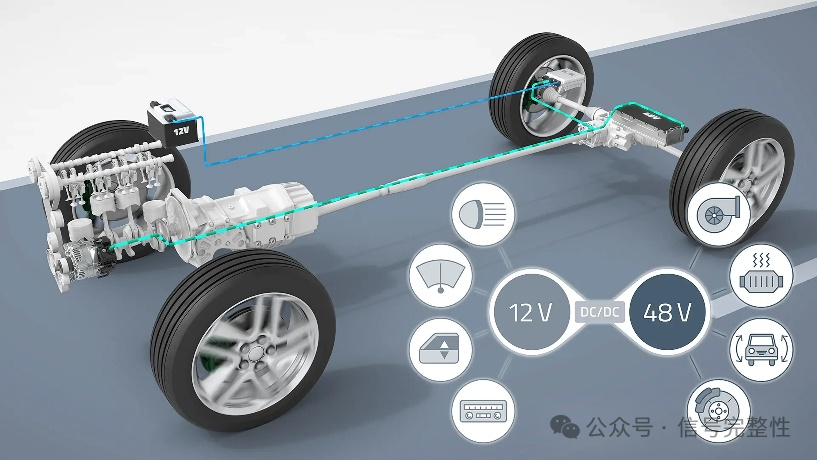
•Traditional fuel vehicles are mainly powered by 12V, but modern electric vehicles and hybrids need higher power, 48V Mild Hybrid system can efficiently drive auxiliary motors, electronic turbines, etc., to improve fuel economy.
•The high voltage (400V, 800V) main drive system still exists, but the 48V system is used for low power loads (such as power steering, air conditioning compressors, etc.), reducing complexity and cost.
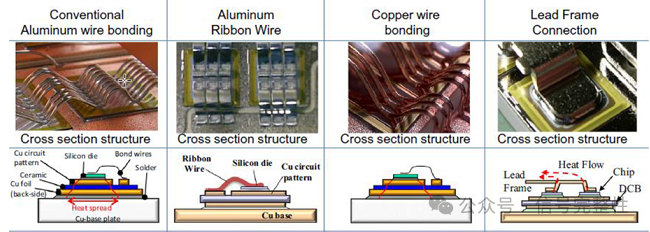
3. Cost and design optimization
•Cables and PCB wiring for 48V systems can use thinner copper wires, reducing copper costs。
•Compared to 12V systems, 48V devices have lower current, which can reduce the size and heat dissipation requirements of power devices (MOSFETs, IGBTs, inductors, etc.)求。
•The conversion efficiency of power converters (such as DC-DC converters) is improved, thereby reducing overall energy consumption。
Comparative analysis of 12V vs. 48V systems
| Contrast dimension | 12V system | 48V system |
| Current and loss | High current, high loss: When transmitting the same power, the current is larger, resulting in increased I²R loss and the need for thicker wires | Current, low loss: at the same power, the current is reduced by 4 times, the loss is reduced by 16 times, and the copper consumption of the wire is reduced |
| Power density | Low: Suitable for low power equipment, more than 1kW power transmission is not efficient | High: Suitable for high-power equipment, more suitable for data centers, electric vehicles, etc |
| Conversion efficiency | Low: High current leads to increased loss of power devices such as MOSFETs and rectifiers | High: Low current reduces wire and power device losses and improves DC-DC conversion efficiency |
| Wiring and design | The cable is thicker and the wiring is complex: thicker cables and larger copper layers of the circuit board are required | Thin cable, routing optimization: reduce the amount of copper wire, reduce the complexity of PCB wiring |
| Application scenario | Suitable for small electronic devices, low power systems (PCS, battery powered devices, etc.) | It is suitable for high-power scenarios such as data centers, servers, electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and industrial equipment |
| security | Safer: Lower human safety voltage (12V is much lower than 60V low voltage safety standard) | Still within the safe range (48V < 60V), but the short-circuit arc energy is higher than 12V, requiring additional protection |
| cost | Low short-term cost: Traditional 12V equipment and ecology mature, low initial cost | Better long-term costs: less copper, more energy efficiency, but higher initial investment |
| Industry trend | Gradually replaced: Gradually replaced by 48V in applications with high power requirements | Rapid growth: 48V solutions are used in data centers, electric vehicles and other fields |
免责声明: 本文章转自其它平台,并不代表本站观点及立场。若有侵权或异议,请联系我们删除。谢谢! Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from other platforms and does not represent the views or positions of this website. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact us to delete it. thank you! |


